Metabolism
In-vivo and in-vitro assays were developed to study effects of drugs or nutrients on glucide and lipid homeostasis or to phenotype diabetes or dyslipidemia
Technology
|
 |
Test 1 : lipid homeostasis
-
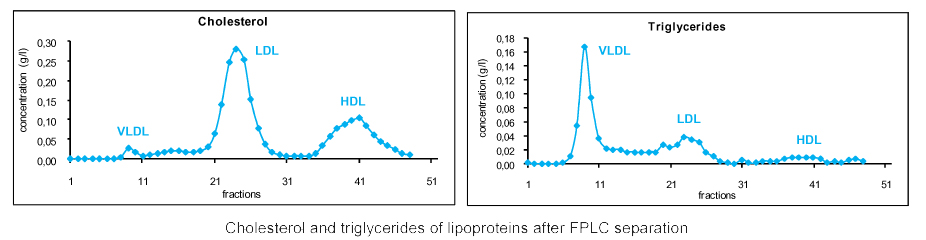
Lipoproteins profiles
Profiles from 200μl (FPLC) or 10μl of plasma (HPLC)
 |
-
Biomarkers
- HDL-C, LDL-C, Total Cholesterol
- AGL, TG, Glycerol
- Insulin, Glucose
- Adipokines
- Inflammatory plasma markers (Luminex® technology)
- PCSK9
- Synthesis (lathosterol) and absorption (phytosterols) markers of cholesterol – plasma/feces – GC-MS
- Biliary acids (CA, CDCA, DCA, LCA, UDCA, α,β,ω muricholic acids) –plasma/feces – GC-MS – UPLC-MS
- Measurement of cholesterol metabolic flux
Measurement of intestinal absorption and trans-intestinal cholesterol excretion (TICE)
Measurement of biliary excretion
Analysis of major regulatory pathways (qPCR, transcriptomics and proteomics)
- Lipoprotein labeling (measurement of lipoporoteins kinetics: catabolism and synthesis)
- TG metabolism
Measurement of postprandial lipemia
Measurement of intestinal and hepatic production of TG-rich particles after lipase treatment
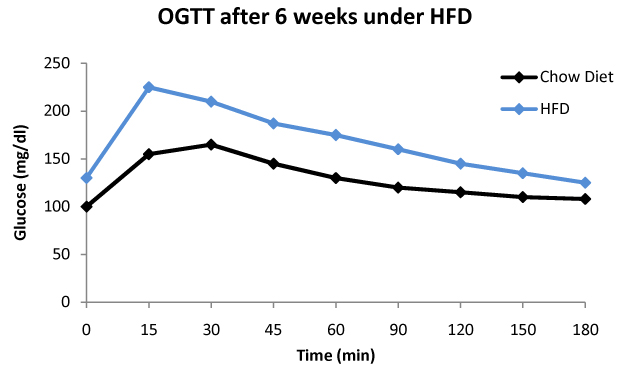
Test 2 : Glucose homeostasis
Test 3 : Metabolic cages
- Energy expenditure
Energy expenditure is estimated by indirect calorimetry by measurement of O2 consumption and CO2 production with highly precise sensors. Respiratory exchange ratio (RER, which define fuel preference between glucose vs. lipid metabolism) and heat production can be calculated. Food and drink consumption can also be followed and animal activity too (actimetry IR).
- Urine and feces production
Urine and feces are collected in metabolic and diuresis cages.
Animal models:
- Hypercholesterolemic Mouse Model: LDLr KO, ApoE KO, PCSK9 KO
- Metabolic Syndrome Model: Mouse under high fat diet (obesity) or fructose / diet deficient diet
choline (steatosis)
- Bariatric Surgery Mouse Model: Sleeve Gastrectomy and Y Gastric Bypass